AGRONOMIC RESOURCESTO SUPPORT EVERY SEASON
YOU CAN TAKETO THE FIELD
LG Seeds’ Corn Scouting Guide
Field-by-Field Agronomic Insights from Emergence to Maturity
Accurate corn staging and consistent field scouting are the foundation of effective agronomic management. Every decision, from herbicide timing to fungicide application, depends on knowing your crop’s growth stage and condition.
This guide brings together LG Seeds’ agronomic expertise to help you identify growth stages, scout effectively, and make confident, data-backed decisions throughout the season.
Corn Staging: What You Should Know
Corn staging isn’t just a technical detail, it’s a critical part of maximizing yield potential. Each stage signals what’s happening developmentally and what actions to take next.
Corn Staging Methods
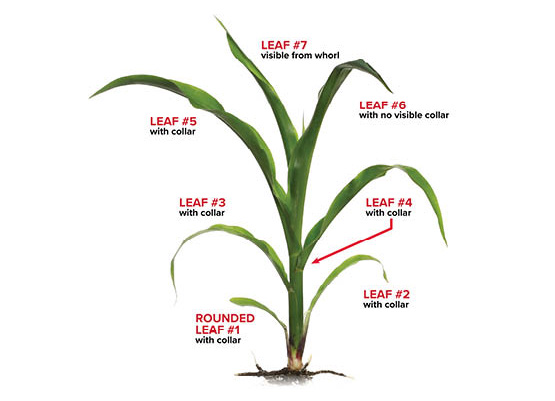
Leaf Collar Method (Recommended)
- How it works: Count only leaves with fully visible collars, starting with the rounded “thumb-shaped” base leaf.
- Pros: Most widely used and required for newer herbicide labels; highly accurate.
- Cons: May undercount compared to droopy-leaf staging.
- Best for: Post-emergence herbicide timing and crop development tracking.
Droopy Leaf Method
- How it works: Counts leaves once they are 50% exposed or droopy, including those still in the whorl.
- Pros: Useful for legacy herbicide references.
- Cons: Can overestimate the growth stage if not applied consistently.
Tip: Match your staging method to your herbicide label. When uncertain, use the leaf collar method and confirm with your agronomist or chemical provider.
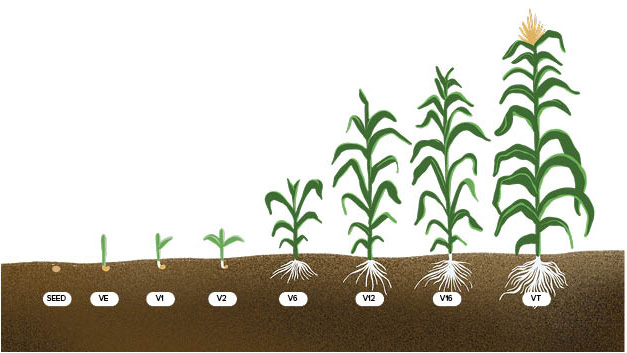
Corn Growth Overview
Corn growth is divided into two major phases:
Phase | Stage Range | Focus |
Vegetative (V) | VE – VT | Leaf, root, and stalk development. Establishing yield potential. |
Reproductive (R) | R1 – R6 | Kernel fertilization and grain fill. Protecting and finishing yield. |
Accurate staging allows you to anticipate when nutrient, pest, or disease pressure is likely to occur and act before yield is lost.
Scouting by Growth Stage
VE to V3 – Early Establishment Checks
At these stages, corn transitions from seed-based energy to the nodal root system.
This is the foundation for stand uniformity and future yield.
Scout For:
- Stand counts and uniform emergence (use 1/1000th-acre method)
- Nutrient deficiencies (purple/yellow leaves)
- Insects: Black cutworm, white grub, seed corn beetle, wireworm
- Diseases: Pythium, Fusarium, Rhizoctonia
- Early-season weeds or crusting
Management Tip: Record planting depth, emergence timing, and spacing to evaluate planter performance. Replant decisions are easiest now, don’t wait.
V4 to V6 – Foundation Building
The growing point rises above the soil at V5–V6, making plants more vulnerable to above-ground injury. This stage sets the foundation for potential yield.
Scout For:
- Nutrient uptake indicators: chlorosis or purpling
- Weed competition and herbicide timing windows
- Insects: Corn rootworm larvae, European corn borer, armyworm
- Disease: Goss’s Wilt, Stewart’s leaf blight
Management Tip: Apply post-emergence herbicides based on staging accuracy, not plant height. This is also an ideal time to sidedress nitrogen.
V7 to VT – Critical Yield Formation
Between V7 and VT, the corn plant defines kernel rows and ear potential. The stalk elongates rapidly, and nutrient demand peaks.
Scout For:
- Drought or heat stress symptoms
- Leaf diseases: Goss’s Wilt, Gray leaf spot, Eyespot, Northern leaf blight
- Insects: Corn rootworm, Japanese beetle, European corn borer
- Weed escapes affecting light or nutrient competition
Management Tip: Nutrient stress between V10–V15 can sharply reduce kernel number. Maintain nitrogen and potassium availability and consider early fungicide planning.
VT – Tasseling
Tasseling marks the transition to reproduction. Silks typically emerge within three days, and pollination follows soon after.
Scout For:
- Tassel-silk synchronization
- Silk clipping by corn earworm or Japanese beetle
- Disease pressure: Tar spot, Common rust, Gray leaf spot
- Heat or drought stress impacting pollination
Management Tip: Apply fungicide between VT and R1 to protect against disease pressure during this critical reproductive window.
R1–R6 – Kernel Development & Harvest Prep
Once pollination is complete, focus turns to kernel development, stalk strength, and grain fill.
Stage | Key Activity | What to Scout For |
R1 (Silking) | Fertilization of kernels | Corn earworm, Western bean cutworm, silk feeding, drought stress |
R2 (Blister) | Kernel formation | Early abortion from drought or disease |
R3 (Milk) | Rapid dry matter accumulation | Heat stress, foliar disease, tip-back |
R4 (Dough) | Kernel weight formation | Stalk rot onset, tar spot |
R5 (Dent) | Kernel hardening | Lodging risk, late disease, standability |
R6 (Maturity) | Black layer formation | Harvest timing, ear retention, hybrid evaluation |

Scouting Techniques and Frequency
- Pattern: Walk in a W or zig-zag pattern for representative coverage.
- Documentation: Use GPS-tagged photos and mobile tools for consistent data logging.
- Technology: NDVI or drone imagery helps identify stress areas across large fields.
- Timing:
- Weekly scouting from emergence through V6
- Increased frequency during VT–R1 for pollination and fungicide decisions
- Biweekly from R3–R5 for harvest preparation
- Weekly scouting from emergence through V6
Always scout after:
- Major rain, wind, or hail events
- Fertilizer or herbicide applications
- Unexplained stress symptoms
Turning Observations Into Action
Scouting delivers value when it informs management. Use your notes to:
- Adjust fertilizer, pesticide, and fungicide timing
- Make replant or rescue treatment decisions
- Track hybrid performance and placement accuracy
- Refine next year’s hybrid selection
Work with your LG Seeds agronomist to connect in-season scouting insights with your long-term hybrid and management plan.
Scouting Tips & Tools
- Use LG Seeds’ staging charts and field-ready checklists
- Scout mid-morning when leaves are dry and collars are visible
- Integrate field notes into Advantage Acre® for year-over-year tracking
- Bring measuring tapes, hand lenses, and reference photos for accuracy
Make Every Observation Count
Scouting isn’t just about spotting problems, it’s about preventing them.
When you understand corn staging and scout with purpose, you gain control over your yield potential.
Every plant, every pass, every season, LG Seeds is here with the agronomy support to help you make every observation count.
Need Help with Staging or Scouting Strategy?
Contact your local LG Seeds agronomist to develop a customized scouting plan that fits your hybrids, field history, and seasonal goals. Connect with an LG Seeds agronomist





